Tips for Teaching Kids About Money Early: Essential Strategies for Financial Literacy
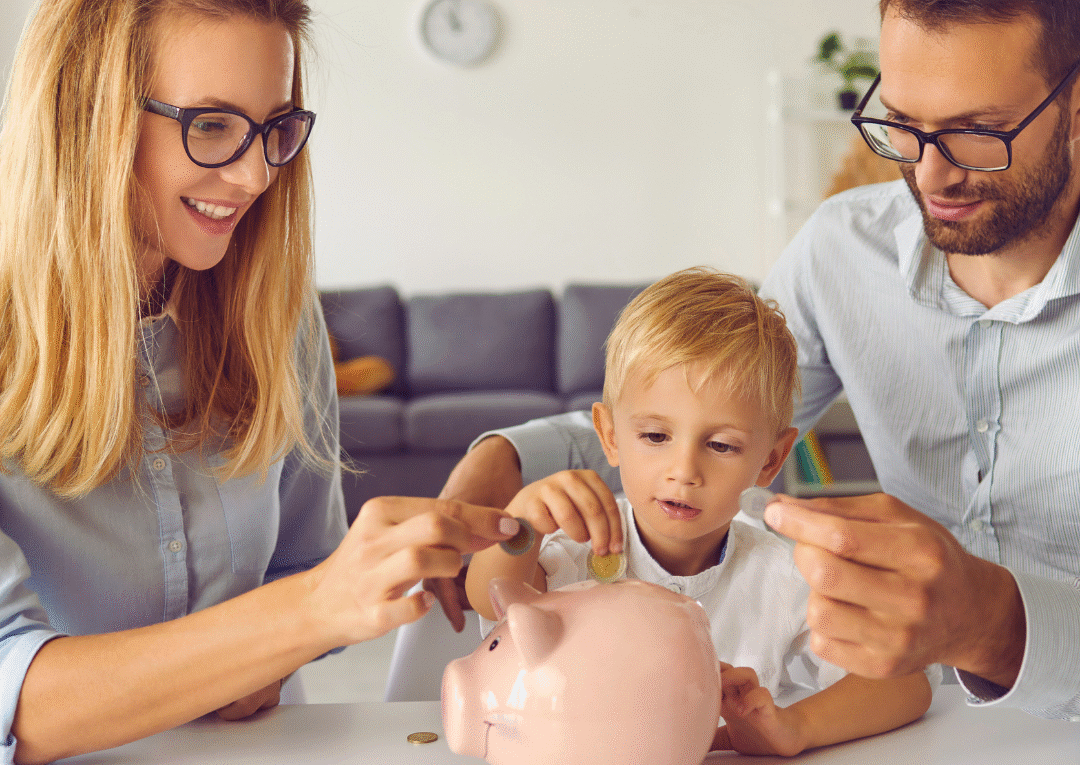
Teaching kids about money early sets the foundation for their financial literacy and responsibility in the future. By integrating simple money management concepts into everyday life, parents can equip children with the tools they need for sound financial decisions. Beginning these conversations at a young age can demystify money and help develop healthy financial habits.
Children can learn through practical experiences, such as budgeting their allowance or saving for a desired toy. Making these lessons fun and engaging encourages them to take an interest in managing money. Early exposure to financial concepts paves the way for informed decisions as they grow.
Creating a safe environment for discussions about money fosters an understanding of its value and implications. When children grasp the basics of earning, spending, and saving, they become more prepared to navigate their financial futures with confidence.
Establishing Financial Foundations with Budgeting
Teaching children about budgeting lays the groundwork for effective money management in their future. Key strategies include the use of allowances and starting savings accounts, both of which encourage responsible financial habits.
The Role of Allowances in Money Management
Allowances serve as a practical tool for children to experience money management firsthand. Assigning a regular allowance, whether weekly or monthly, helps children learn to budget their funds.
Parents can establish guidelines to encourage wise spending decisions, emphasizing the importance of saving a portion. A common rule is the 50/30/20 breakdown: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings.
By tracking spending through simple tools like a notebook or budgeting app, kids gain insights into their financial choices. This practice fosters accountability and helps them understand the value of money.
Starting a Savings Account for Kids
Opening a savings account is a crucial step in teaching children about saving money. A savings account not only provides a safe place for kids to keep their earnings but also introduces them to banking concepts.
Parents should look for accounts with no fees and competitive interest rates. It’s essential to involve children in the account setup process, explaining how deposits and interest work.
Encouraging regular deposits, such as a portion of their allowance or money received as gifts, reinforces the habit of saving. Setting savings goals can transform saving money into an engaging activity. This strategy teaches kids the significance of financial planning and the rewards of watching their money grow over time.
Practical Money Skills through Hands-On Learning
Engaging children in hands-on activities can significantly enhance their understanding of money management. Practical experiences help them grasp concepts like saving, spending wisely, and recognizing value in everyday situations.
Teaching through a Piggy Bank System
Using a piggy bank provides a visual and tactile way for children to learn about saving. Parents can encourage kids to allocate their allowance or earnings into different sections: savings, spending, and donations.
This method can be tracked with a simple chart that shows progress. For instance, kids can mark their savings goal and visually see their accumulation grow over time. By fulfilling specific savings goals, they can experience the satisfaction of watching their efforts pay off.
Making Smart Spending Choices
Teaching children to make informed spending choices is crucial. Parents can initiate discussions about needs versus wants. For instance, create a list of items to buy and categorize them accordingly.
Role-playing shopping scenarios can be beneficial. Parents may give a child a small budget and ask them to select items that fit within it. This practice teaches the importance of budgeting and prioritizing.
Understanding Value during Grocery Shopping
Grocery shopping offers excellent opportunities for children to learn about money value. Parents can involve children in comparing prices of similar products while at the store. This comparison teaches them to look for better deals.
Using a shopping list can help children understand how to plan and stick to a budget. Additionally, discussing unit prices and sales can reinforce the idea of making informed purchasing decisions. This practice encourages critical thinking about money in real-world situations.
Setting and Achieving Financial Goals
Teaching kids to set and achieve financial goals fosters essential financial habits. It encourages responsibility and enhances their understanding of money management principles.
Learning to Set Short and Long-Term Goals
To begin, children should learn the difference between short-term and long-term financial goals. Short-term goals are achievable within a year, like saving for a toy. Long-term goals need more planning, such as saving for a bicycle or college tuition.
Using a SMART criteria framework can be effective:
- Specific: Define clear objectives (e.g., “Save $50 for a game”).
- Measurable: Track progress (e.g., $10 a month).
- Achievable: Ensure goals are realistic based on income or allowances.
- Relevant: Align goals with interests (e.g., saving for video games).
- Time-bound: Set deadlines for completion.
This structured approach helps children understand how to set meaningful goals.
Guidance on Prioritizing Financial Goals
Once goals are established, prioritizing them is crucial. Kids should learn to evaluate which goals are most important based on factors like urgency and impact. Asking guiding questions can help:
- Which goal excites them the most?
- Which goal will benefit them in the long run?
Creating a list can aid in organization. For example:
- Save for a game (short-term)
- Save for a new bike (long-term)
- Start a college fund (very long-term)
Prioritizing helps children focus their efforts and develop patience as they work toward their dreams. It instills a sense of discipline, shaping strong financial habits for the future.