Tips for Making Education More Inclusive: Strategies for Diverse Learning Environments
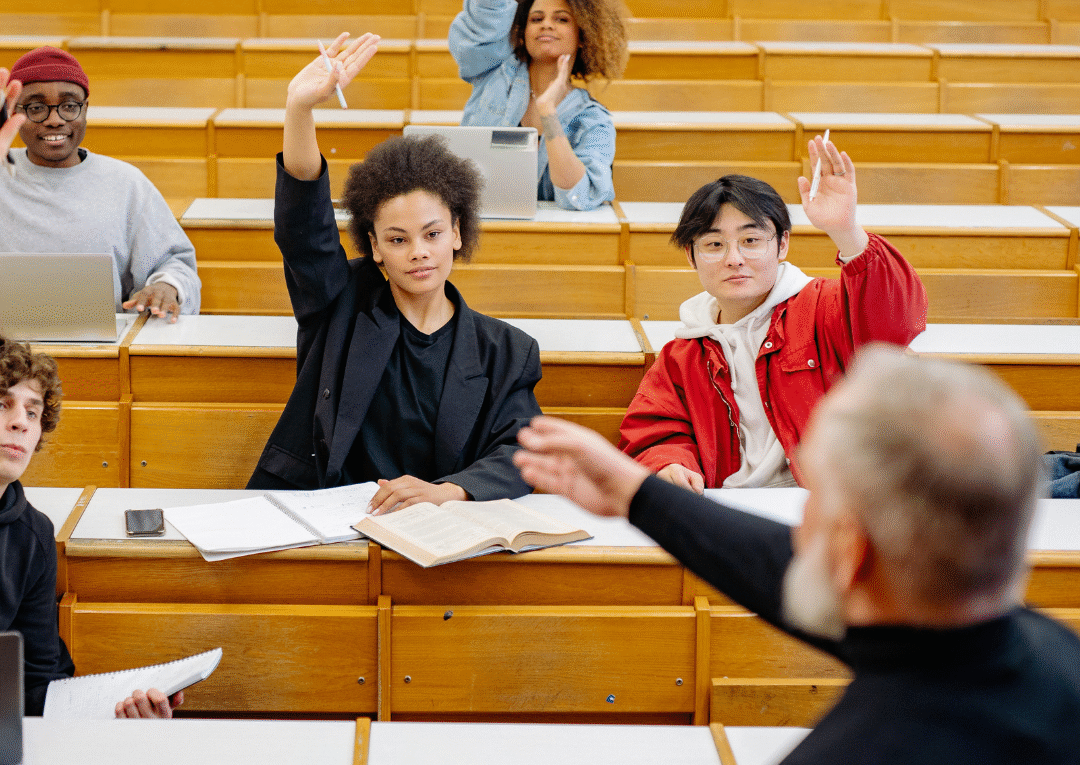
Education plays a crucial role in shaping society, and making it more inclusive benefits everyone. By implementing diverse teaching strategies and fostering an environment where every student feels valued, educators can ensure that all learners have equal opportunities to thrive. These strategies not only support students with varying needs but also enrich the learning experience for the entire classroom.
Incorporating universal design principles and adapting materials can significantly enhance accessibility. Educators can embrace technology and collaborative learning techniques to engage all students, creating a classroom culture that celebrates differences and promotes collective growth.
Building strong relationships among students and between students and teachers is essential. When educators actively listen and respond to individual needs, they create a foundation of trust and respect, allowing for a more inclusive and effective educational environment.
Establishing an Inclusive Classroom
Creating an inclusive classroom involves understanding the principles of inclusive education and designing a supportive learning environment. This fosters engagement and ensures that all students can thrive.
Understanding Inclusion in Education
Inclusion in education means providing equal access to learning for all students, regardless of their background or individual needs. Effective inclusive classrooms recognize the diversity of students, incorporating various teaching methods tailored to different learning styles.
Key components include:
- Equity: Ensuring every student has the resources they need to succeed.
- Respect: Valuing each student’s unique contributions and perspectives.
- Collaboration: Encouraging teamwork among students to foster a sense of community.
Inclusion is not merely about physical presence in the classroom; it emphasizes the active participation of all students in the learning process.
Designing an Inclusive Learning Environment
Designing an inclusive learning environment requires attention to physical space and the use of Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles. The classroom layout should allow for flexibility, incorporating diverse seating arrangements that support collaboration and individual learning.
Essential elements include:
- Accessible Resources: Providing materials in various formats (audio, visual, tactile).
- Assistive Technology: Utilizing tools that support students with disabilities.
- Flexible Curriculum: Adapting lessons to meet the needs of all learners.
An inclusive environment encourages positive interactions among students, fostering a respectful atmosphere where everyone feels valued and engaged.
Inclusive Teaching Strategies
Implementing effective inclusive teaching strategies addresses the varied needs of students, enabling them to thrive in diverse learning environments. Key areas to focus on include adapting teaching methods, enhancing communication, and modifying course materials.
Adapting Teaching Methods for Diversity
Tailoring teaching methods to accommodate diverse learning styles is crucial. Teachers can implement a mix of instructional approaches, such as:
- Direct instruction for students who benefit from structured guidance.
- Collaborative learning that encourages teamwork and peer interaction.
- Hands-on activities to support kinesthetic learners.
Incorporating technology can also aid in inclusivity. Tools like online platforms allow students to learn at their own pace. Teachers should regularly assess the effectiveness of these methods and adjust them to better meet students’ unique needs.
Classroom Communication and Participation
Effective communication fosters an inclusive classroom environment. Establishing clear expectations for participation is essential. Strategies for enhancing communication include:
- Utilizing visual aids to reinforce verbal instructions.
- Offering multiple ways for students to participate, such as through written responses or digital tools.
- Encouraging a culture of respect where all voices are valued.
Regular feedback is vital. Teachers should create opportunities for students to express their thoughts and experiences concerning classroom dynamics. This can lead to increased engagement and a sense of belonging.
Course Materials and Curriculum Adaptation
Adapting course materials ensures all students can access learning. It is essential to provide a variety of resources, such as:
- Textbooks in different formats (e.g., audio, digital).
- Supplementary materials that reflect diverse perspectives.
Incorporating diverse examples and case studies helps students connect with the content. Teachers should also involve students in selecting resources, as this boosts ownership and interest. Continuous evaluation of materials ensures they remain relevant and effective for all learners.
Supporting Diverse Learners
Creating an inclusive educational environment requires a nuanced approach to support diverse learners. This involves understanding various needs related to disability, cultural backgrounds, and promoting a growth mindset among all students.
Addressing Disability and Neurodiversity
It is essential to recognize and accommodate disabilities and neurodiverse conditions such as autism spectrum disorder. Schools should implement Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) tailored to each student’s needs.
Providing assistive technology, specialized teaching methods, and a structured environment will help these learners thrive. Training educators to understand neurodiversity helps create a supportive atmosphere.
Regular assessments can track progress and adapt strategies as necessary. Open communication with students and families supports transparency and collaboration, fostering a sense of belonging.
Cultural and Ethnic Considerations
Education must also reflect the diverse cultural and ethnic backgrounds of learners. Recognizing the significance of religion and socioeconomic factors is critical in shaping a student’s experience.
Curricula should include diverse perspectives and authors to foster connection and representation. Schools can celebrate cultural events and encourage discussions that promote understanding and respect for different backgrounds.
Additionally, partnerships with local communities can enhance relevance and engagement. Providing resources in multiple languages ensures that non-native speakers receive equitable support.
Empowering through a Growth Mindset
Adopting a growth mindset is vital for encouraging resilience in students. It promotes the belief that abilities and intelligence can develop with effort, leading to increased motivation and perseverance.
Educators should model growth mindset principles by sharing personal experiences of challenges and learning. Constructive feedback should be emphasized, focusing on effort rather than inherent ability.
Incorporating goal-setting activities helps students envision their potential. Celebrating progress, no matter how small, reinforces the belief that improvement is possible for everyone.
Evaluating Success and Continuous Improvement
Assessing the effectiveness of inclusive education requires a focus on measuring learning outcomes and fostering a supportive classroom community. These elements are essential for ensuring that all students have equal access to educational opportunities and motivation to succeed.
Measuring Learning Outcomes
Effective evaluation of learning outcomes is crucial for determining the success of inclusive education strategies. Educators should employ a variety of assessment methods, including formative assessments, standardized tests, and project-based evaluations, to gather comprehensive data on student performance.
- Diverse Assessments: Utilize multiple types of assessments to cater to different learning styles.
- Data Analysis: Analyze data to identify patterns and areas needing improvement.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish regular feedback loops between students and educators to ensure clarity in expectations.
By measuring learning outcomes more accurately, educators can identify gaps in understanding and adjust instruction accordingly.
Fostering a Supportive Classroom Community
Creating an inclusive classroom community enhances student engagement and motivation. A supportive environment encourages collaboration and respect among peers.
- Peer Support Systems: Implement buddy systems or peer tutoring for students needing additional help.
- Inclusive Practices: Promote activities that celebrate diversity and ensure everyone feels valued.
- Open Communication: Encourage dialogue among students to foster empathy and understanding.
These strategies are integral to cultivating an atmosphere where every student feels they belong, ultimately leading to improved educational outcomes.